How to Eliminate Static Electricity of Tanker Trucks
How to Eliminate Static Electricity of Tanker Trucks
Static electricity poses a serious ignition risk during the loading and unloading of flammable liquids in tanker trucks. Proper mitigation measures are critical to ensure safety:
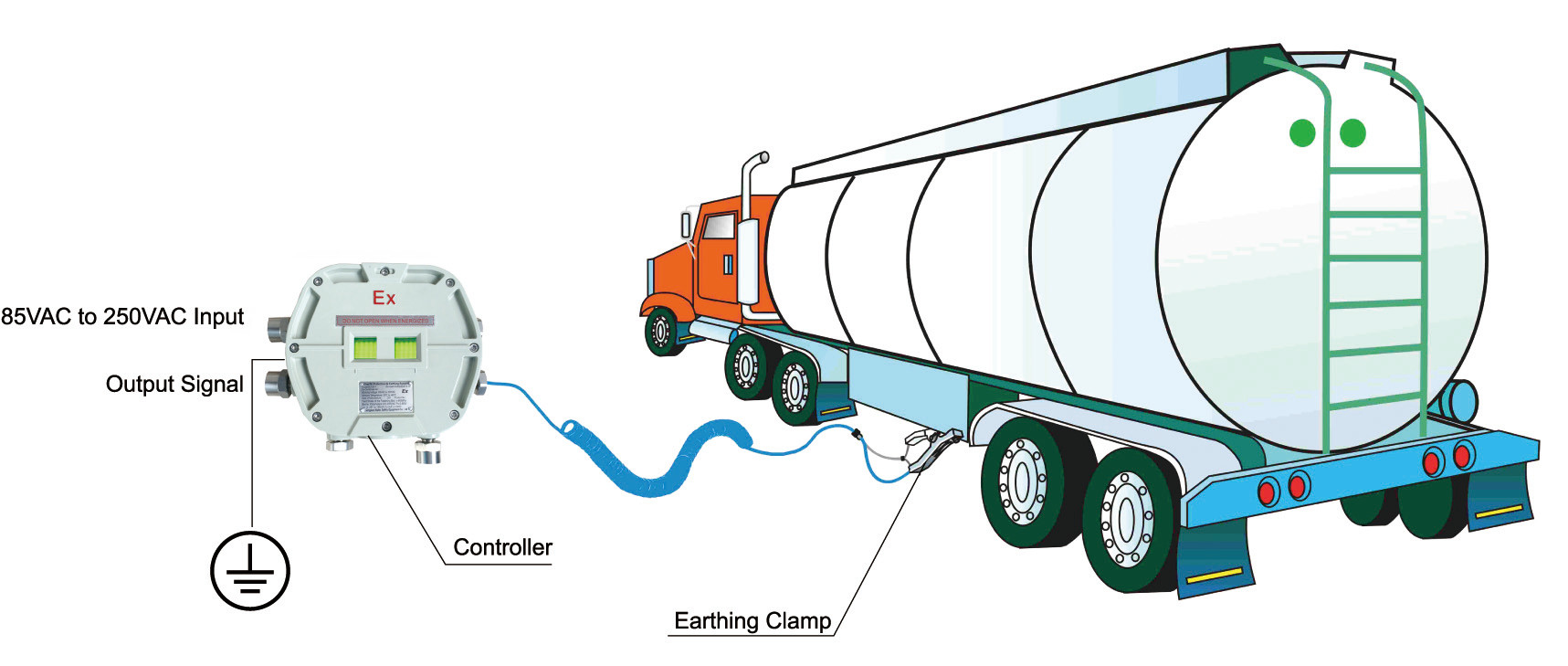
1. Grounding and Bonding: Always connect the tanker to a grounding system before operations. Use conductive cables to bond the truck to the loading rack, ensuring electrical continuity and dissipating static charges.
Our grounding system is ATEX certified, almost free maintenance.
2. Control Flow Rates: High fluid velocity increases static buildup. Maintain recommended flow rates (typically below 1 m/s) during loading, especially during the initial phase when the tank is empty.
3. Avoid Splashing: Use submerged filling pipes or bottom-loading systems to minimize splashing, which generates static electricity.
4. Cleanliness: Remove debris, rust, or residues inside tanks, as particles can create friction-induced charges. Ensure non-conductive contaminants (e.g., water droplets) are minimized.
5. Conductive Materials: Use conductive hoses and equipment to prevent charge accumulation. Regularly inspect for wear or damage.
6. Personnel Training: Operators should wear anti-static footwear and clothing. Prohibit activities that generate sparks (e.g., using mobile devices) during operations.
7. Environmental Monitoring: In dry conditions, consider humidity control systems or anti-static additives for liquids to enhance conductivity.
Post-operation, allow a 30 --minute "relaxation period" before disconnecting grounding equipment to ensure residual charges dissipate. Regular equipment inspections and adherence to safety protocols (e.g., API RP 2003, NFPA 77) are essential to prevent static-related incidents.