Safety hazard of clothing fabrics in gas station safety
The
level of the human body's electrostatic potential has an important relationship
with clothing (including footwear). During production activities, the human
body and clothing are often charged at the same time. If the electrostatic
potential on the clothing reaches a certain level, electrostatic discharge will
also occur, but the calculation formula of its discharge energy is different
from that of the human body. The discharge formula of the conductor cannot be
used, but the following formula is used:
E=1/2KσV
In
the formula:
E—discharge
energy of clothing or fabric;
K—constant,
in actual calculation, the constant K often takes 0.02;
σ—charge
density on the surface of clothing or fabric, μC/m2;
V—Electric
potential on the surface of clothing or fabric.
Scholars
have conducted years of research on the ignitability of electrostatic discharge
of clothing fabrics. Wilson put forward a special test report on the
ignitability of electrostatic discharge of clothing fabrics in 1985. It shows
that the polyester chemical fiber fabric with negative charge has a brush
discharge under certain conditions at moderate ambient humidity (50% relative
humidity), which is enough to ignite natural gas or a mixed combustible gas of
hydrogen and air. For cotton fabrics, when the relative humidity of the
environment is 15% or 33% (not at 50%), the discharge with negative charge is
enough to ignite the above-mentioned combustible gas.
There
have been reports in China that during the removal of nylon yarn, electrostatic
discharge was caused, which caused the liquefied gas to catch fire. There are
cases where the anti-gas mask (made of plastic) is released to cause burning.
There are also electrostatic discharge accidents caused by clothes sorting, hat
removal and other operations.
The
following describes the results of a set of comparative tests by the Beijing
Institute of Labor Protection Science. That is, wear ordinary clothes and
anti-static clothing, stand on different grounds, conduct undressing
electrification test at the same time, and then compare.
(1)
The experimenter wears insulated shoes, stands on insulated ground, and wears
ordinary clothes. Then take off the outer jacket and immediately use it to
touch the potentiometer contacts to measure the human body potential; at the
same time, put the removed jacket on the rope and measure the electric potential
of the clothes. The results are shown in the table below.
Table
1 Results of ordinary clothes undressing
electrification test
|
Tester |
Material
of inner and outer clothing |
Body
electric potential(V) |
Clothes
electric potential(V) |
Remark |
|
A |
Wearing
dacron coat Wear
blue jeans Under
wearing sweater |
4800 |
28000 |
Temperature
15℃ Humidity
40% Body
capacitance C-A:
130pf C-B:
130pf |
|
4200 |
20800 |
|||
|
5300 |
29000 |
|||
|
B |
Wearing
elastic coat Wearing
wool pants Under
wearing silk cotton Under
wearing nylon pants |
6400 |
42300 |
|
|
6400 |
35000 |
|||
|
6100 |
28000 |
(2)
The experimenter wears ordinary clothes inside, and wears anti-static overalls
(suits) on the insulated ground, wears insulated shoes, and performs the
undressing electrification test as above. The test results are shown in the
table below.
Table
Electrification test results of undressing for ordinary underwear and external
anti-static suit
|
Teste |
Material
of inner and outer clothing |
Body
electric potential(V) |
Clothes
electric potential(V) |
Note |
|
A |
Wearing
sweater Wearing
blue jeans |
1300 |
2900 |
Temperature
15℃ Humidity
40% Body
capacitance C-A:
130pf C-B:
130pf |
|
1000 |
2800 |
|||
|
B |
Wearing
sweater Wearing
wool pants |
1300 |
4000 |
|
|
900 |
3800 |
The
test results show that the potential when wearing and removing anti-static work
clothes is indeed much lower than that when wearing ordinary clothes, and the
anti-static effect is remarkable.
However,
even when wearing anti-static work clothes, do not do large-scale actions such
as wearing, taking off, or squatting at any time in a dangerous place to
prevent the occurrence of static accidents.
(The
above content is excerpted from "Industrial Static Electricity" of
China Petrochemical Press)
It
can be seen that the concept of human body static electricity includes not only
the static electricity carried by the human body, but also the static
electricity carried by clothing fabrics. Human body discharge is a conductor
discharge, and its ignition ability is stronger than the static electricity of
clothes and fabrics.
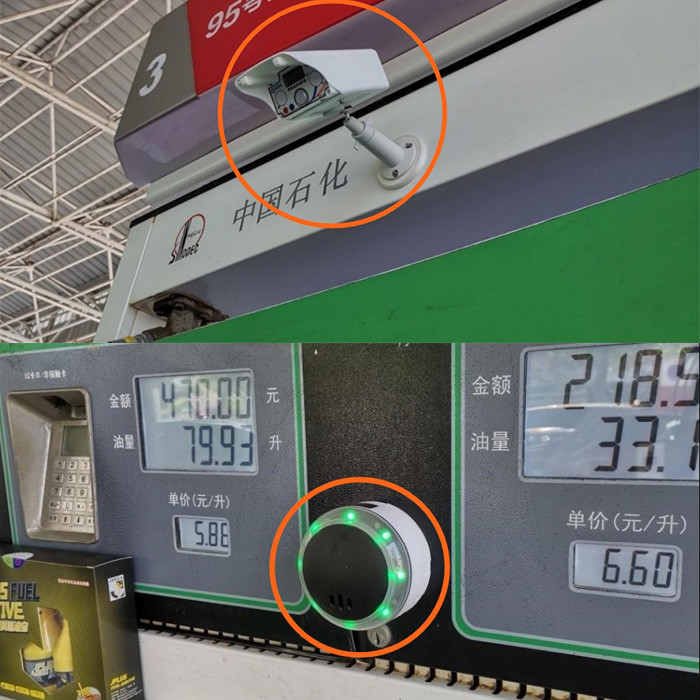
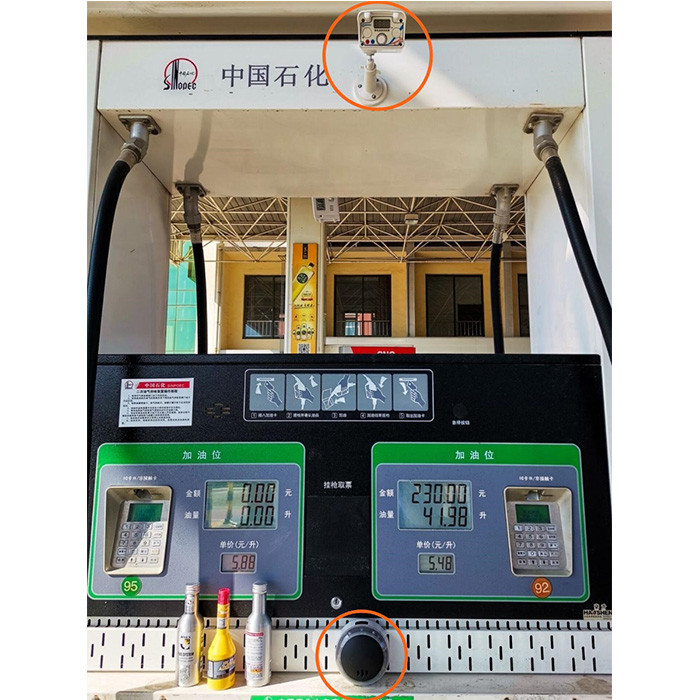
The
following is an example of the installation of static monitors introduced by
Sinopec to prevent static accidents at gas stations.
(An
electrostatic monitor is installed on the top of the tanker to detect static
electricity in the covered area; a static eliminator is installed in the middle
of the tanker to eliminate static electricity and provide visible and audible reminders.)